Welcome to CHETNA 100 Indian Cities
Data-driven research and analysis for understanding India's progress across various sectors
100 Cities Total
2020
2021
2022
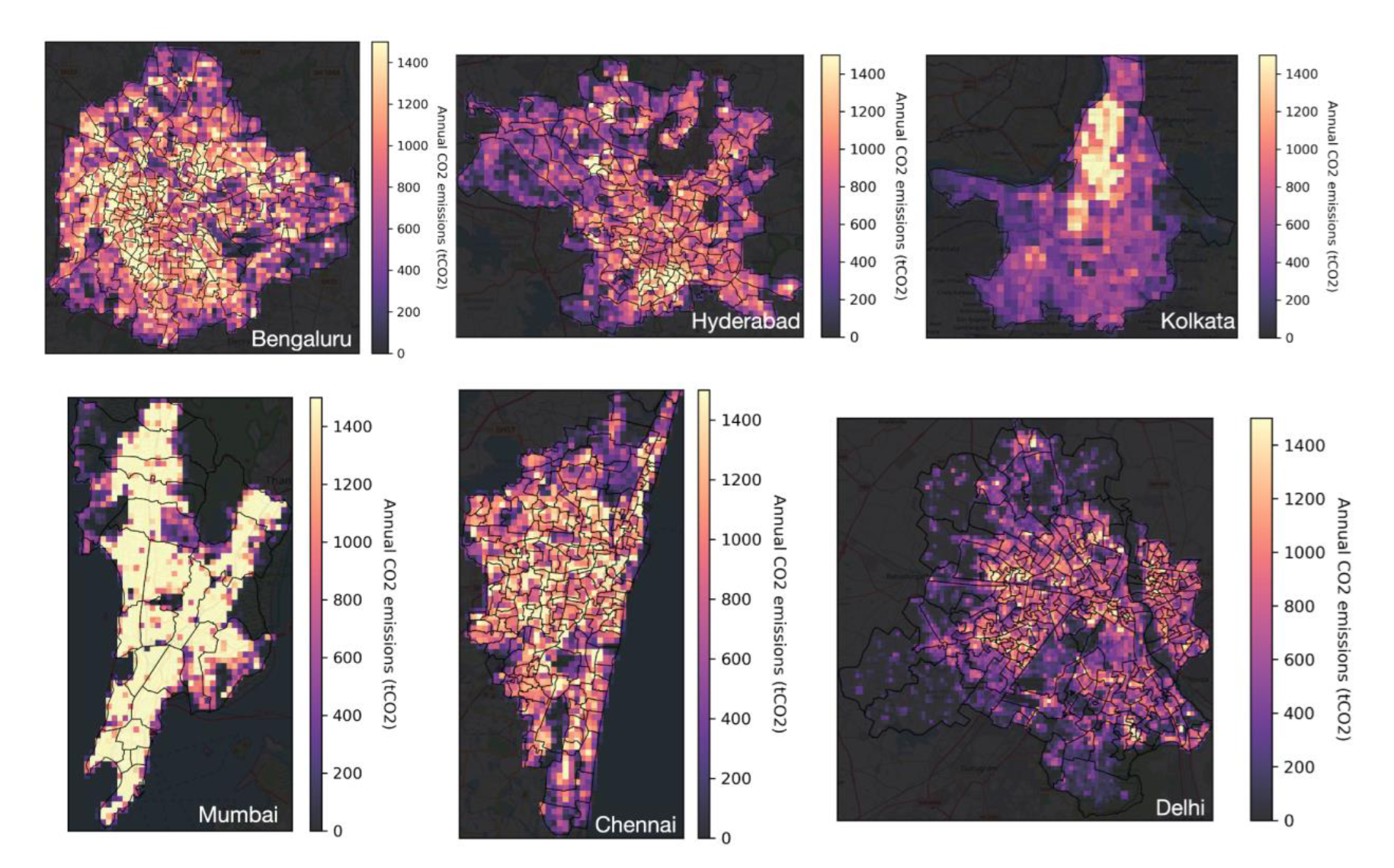
Download CHETNA Emission Dataset
Access comprehensive emission data for Indian cities with time series and gridded map data.
Total
Time Series Data